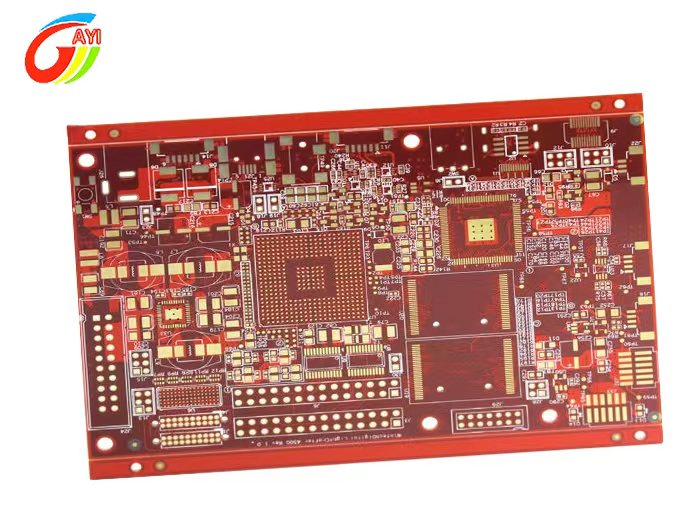
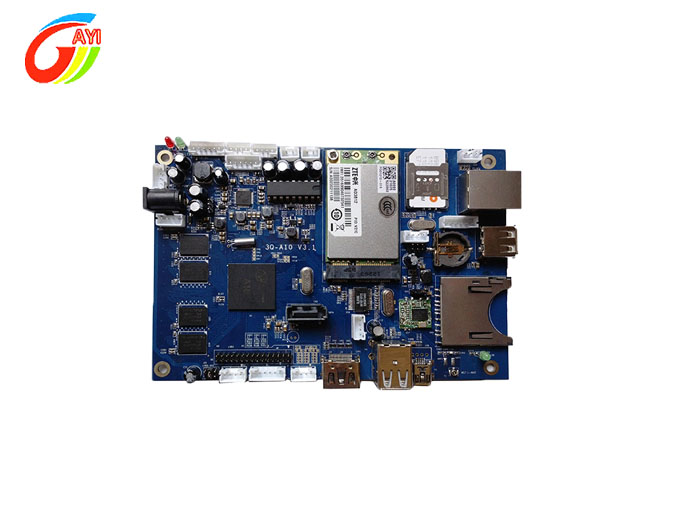
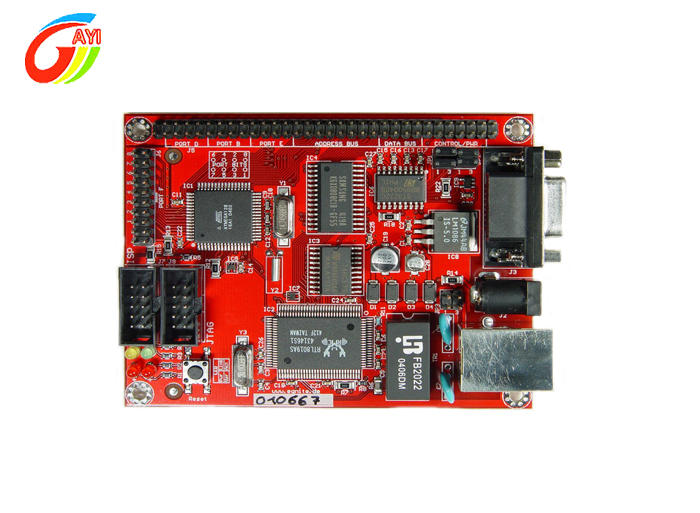
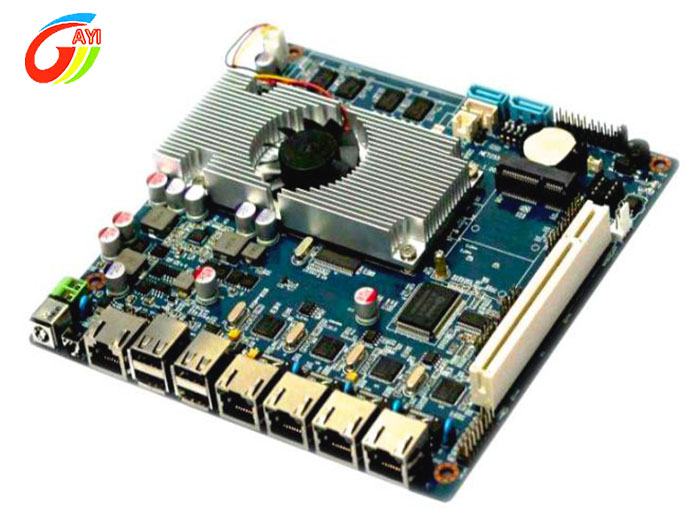
PCB board partition is mainly divided into three types :
Single layer board On the most basic PCB, the parts are concentrated on one side, and the wires are concentrated on the other side. This PCB is called Single layer board because the wire only appears on one side. Because the single panel has many strict limitations in the design of the circuit (because there is only one side, the lines cannot be crossed, and a separate path must be bypassed), only early circuits used such boards.
Double-sided board This circuit board has traces on both sides, but to use the lines on both sides, there must be an appropriate circuit connection between the two sides. This ' bridge ' between circuits is called a via. A through-hole is a small hole in a PCB, filled or coated with a metal four-layer circuit board design that can be connected to wires on both sides. Because the area of the double-sided board is twice that of the single panel, and because the wiring can be interleaved with each other (can be wound to the other side), it is more suitable for use in a circuit that is more complex than a single panel.
Multi-Layer board In order to increase the area that can be routed, multi-layer boards use more single-sided or double-sided routing boards. A printed circuit board with a double-sided inner layer and two single-sided outer layers or two double-sided inner layers and two single-sided outer layers is alternately connected through the positioning system and the insulating adhesive material. The conductive pattern is printed. The circuit board that is interconnected according to the design requirements becomes a four-layer and six-layer printed circuit board, also known as a multi-layer printed circuit board.


 Contact Us Today
Contact Us Today